In the world of international banking and financial transactions, communication is key. One of the most critical components of this communication is the MT202 message. Whether you’re a financial professional, a business owner dealing with international payments, or just someone curious about how money moves across borders, understanding MT202 messages is essential. In this blog post, we’ll break down what MT202 messages are, how they work, and their real-life applications.
Table of Contents
What is an MT202 Message?
An MT202 message is a type of SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) message used for transferring funds between banks. It is specifically designed for interbank payments, meaning it facilitates the movement of money from one bank to another, often in different countries.
The MT202 message is part of the SWIFT MT (Message Type) series, which standardizes financial communication globally. It is commonly used in scenarios where a bank needs to send funds to another bank without involving the underlying customer details. This makes it a crucial tool for banks to settle payments efficiently.
How Does an MT202 Message Work?
To better understand the flow of an MT202 message, let’s visualize the process:
- Sender Bank (Bank A): The bank initiating the payment creates an MT202 message. This message includes details such as the amount to be transferred, the beneficiary bank (Bank B), and any relevant reference numbers.
- SWIFT Network: The MT202 message is sent securely through the SWIFT network, which acts as the intermediary between Bank A and Bank B.
- Receiver Bank (Bank B): The beneficiary bank receives the MT202 message and processes the payment. The funds are then credited to the account of the beneficiary bank.
Here’s a simple diagram to illustrate the flow:
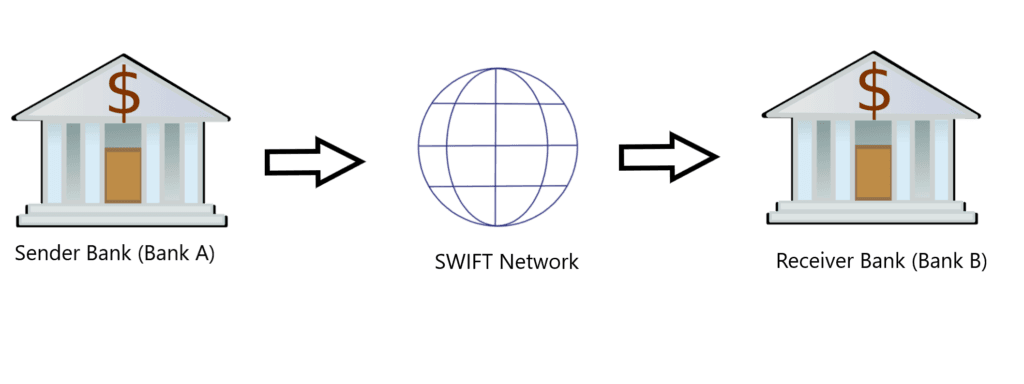
Sender Bank (Bank A) → MT202 Message → SWIFT Network → Receiver Bank (Bank B)Key Fields in an MT202 Message
An MT202 message contains several mandatory and optional fields. Here are some of the most important ones:
- Field 20: Transaction Reference Number (unique identifier for the transaction).
- Field 21: Related Reference (links the MT202 to other messages, such as an MT103).
- Field 32A: Value Date and Amount (the date and amount of the transfer).
- Field 52a: Ordering Institution (the bank initiating the payment).
- Field 58a: Beneficiary Institution (the bank receiving the payment).
For complete swift guide you can check here.
Different Scenarios for MT202 Messages
MT202 messages are versatile and used in various scenarios. Let’s explore some of the most common ones:
1. Interbank Transfers
- When one bank needs to send funds to another bank, an MT202 message is used. This is often seen in correspondent banking relationships, where banks maintain accounts with each other to facilitate international payments.
2. Settlement of Foreign Exchange Transactions
- After a foreign exchange transaction, banks use MT202 messages to settle the funds between themselves.
3. Loan Disbursements
- When a bank disburses a loan to another financial institution, an MT202 message is used to transfer the funds.
4. Clearing and Settlement Systems
- MT202 messages are used in clearinghouses and settlement systems to move funds between participating banks.
5. Customer Payments (Indirect)
- While MT202 messages don’t include customer details, they can be linked to customer payments (e.g., MT103 messages) to facilitate the underlying transaction.
Real-Life Examples of MT202 Messages with SWIFT Messages
To make this more relatable, let’s look at some real-life examples of MT202 messages, including SWIFT message formats:
Example 1: International Trade
- A company in Germany imports goods from a supplier in Japan. The German company’s bank sends an MT202 message to the Japanese supplier’s bank to settle the payment. Here’s how it works:
Actual SWIFT MT202 Message:
{1:F01DEUTDEFFAXXX1234567890}
{2:O2021234567890}
{3:{108:TRN123456}}
{4:
:20:TRN123456
:21:REF987654
:32A:231015USD100000,
:52A:DEUTDEFF
:58A:BOTKJPJT
-}- Field 20: TRN123456 (Transaction Reference Number)
- Field 21: REF987654 (Related Reference)
- Field 32A: 231015USD100000 (Value Date: 2023-10-15, Amount: USD 100,000)
- Field 52A: DEUTDEFF (Ordering Institution: Deutsche Bank, Germany)
- Field 58A: BOTKJPJT (Beneficiary Institution: Bank of Tokyo, Japan)
Example 2: Correspondent Banking
- A bank in Brazil needs to send funds to a bank in South Africa. Since they don’t have a direct relationship, they use a correspondent bank in the US. The Brazilian bank sends an MT202 to the US correspondent bank, which then forwards the funds to the South African bank. Here’s the flow:
Actual SWIFT MT202 Message:
{1:F01BRASBRRJAXXX9876543210}
{2:O2029876543210}
{3:{108:TRN789012}}
{4:
:20:TRN789012
:21:REF654321
:32A:231015EUR50000,
:52A:BRASBRRJ
:58A:CHASUS33
-}- Field 20: TRN789012 (Transaction Reference Number)
- Field 21: REF654321 (Related Reference)
- Field 32A: 231015EUR50000 (Value Date: 2023-10-15, Amount: EUR 50,000)
- Field 52A: BRASBRRJ (Ordering Institution: Banco do Brasil, Brazil)
- Field 58A: CHASUS33 (Beneficiary Institution: JPMorgan Chase, USA)
Example 3: Foreign Exchange Settlement
- A bank in the UK sells USD to a bank in France. After the trade is executed, the UK bank sends an MT202 message to transfer the USD to the French bank’s account. Here’s how it works:
Actual SWIFT MT202 Message:
{1:F01BARCGB22AXXX5678901234}
{2:O2025678901234}
{3:{108:TRN345678}}
{4:
:20:TRN345678
:21:REF876543
:32A:231015USD75000,
:52A:BARCGB22
:58A:BNPAFRPP
-}- Field 20: TRN345678 (Transaction Reference Number)
- Field 21: REF876543 (Related Reference)
- Field 32A: 231015USD75000 (Value Date: 2023-10-15, Amount: USD 75,000)
- Field 52A: BARCGB22 (Ordering Institution: Barclays Bank, UK)
- Field 58A: BNPAFRPP (Beneficiary Institution: BNP Paribas, France)
Example 4: Loan Disbursement
- A multinational corporation secures a loan from a bank in Switzerland. The Swiss bank uses an MT202 message to disburse the loan amount to the corporation’s bank in Singapore. Here’s the process:
Actual SWIFT MT202 Message:
{1:F01UBSWCHZHAXXX3456789012}
{2:O2023456789012}
{3:{108:TRN901234}}
{4:
:20:TRN901234
:21:REF123456
:32A:231015CHF200000,
:52A:UBSWCHZH
:58A:DBSASGSG
-}- Field 20: TRN901234 (Transaction Reference Number)
- Field 21: REF123456 (Related Reference)
- Field 32A: 231015CHF200000 (Value Date: 2023-10-15, Amount: CHF 200,000)
- Field 52A: UBSWCHZH (Ordering Institution: UBS, Switzerland)
- Field 58A: DBSASGSG (Beneficiary Institution: DBS Bank, Singapore)
Why Are MT202 Messages Important?
MT202 messages play a vital role in the global financial system for several reasons:
- Efficiency: They enable fast and secure transfers between banks, reducing the time and cost associated with international payments.
- Standardization: By using a standardized format, MT202 messages ensure clarity and consistency in financial communication.
- Traceability: Each MT202 message includes a unique reference number, making it easy to track and reconcile transactions.
Common Challenges with MT202 Messages
While MT202 messages are incredibly useful, they are not without challenges:
- Lack of Customer Details: Since MT202 messages don’t include customer information, they can sometimes lead to delays in identifying the underlying transaction.
- Errors in Fields: Incorrect or missing data in the MT202 fields can result in failed or delayed transactions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Banks must ensure that MT202 messages comply with international regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) requirements.
Conclusion
MT202 messages are the backbone of interbank payments, enabling seamless and secure transfers across borders. Whether it’s settling a foreign exchange transaction, disbursing a loan, or facilitating international trade, MT202 messages ensure that funds move efficiently between banks.
Understanding how MT202 messages work, their key fields, and their real-life applications can help businesses and financial professionals navigate the complexities of international payments. As the global financial system continues to evolve, MT202 messages will remain a critical tool for banks worldwide.
In next post, we will discuss about MX conversion of MT202 to pacs.009.
Want to know about sepa payment and AUD payment
Sure. Those will be covered in the upcoming articles. Do subscribe.