Introduction: Navigating International Payments with SWIFT MT103
In today’s global economy, businesses and banks rely on the SWIFT MT103 message for secure international fund transfers. But what happens when banks don’t have a direct relationship? That’s where MT202 cover payments come into play.
Make sure you have checked previous posts to understand what is MT103 and MT202 messages.
This comprehensive guide explains:
- What MT103 announcement and cover messages are
- Why cover payments are crucial in global banking
- Real-world SWIFT message examples
- Key differences between serial and cover payments
- When a cover payment is mandatory
- The modern ISO 20022 (MX) equivalent
- Major advantages of using cover messages
Table of Contents
Understanding SWIFT MT103 Announcement Messages
What is an MT103 Announcement Message?
The MT103 is the workhorse of international payments, containing:
- Sender and beneficiary details
- Payment amount and currency
- Transaction references
- Settlement instructions
What is a MT202 Cover Payment?
When banks need an intermediary to complete a transaction, they use:
- MT103 – Contains customer payment details
- MT202 COV – Handles the interbank fund settlement
Why Cover Payments Are Essential
Cover payments solve critical challenges in cross-border transactions:
1. Bridging Banking Relationships
🌐 Problem: Only about 25% of global bank pairs have direct relationships
✅ Solution: Cover payments enable transactions between any banks via intermediaries
2. Compliance & Security
🛡️ Benefit: Intermediary banks perform:
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks
- Sanctions screening
- Fraud prevention
3. Currency Conversion
💱 Example: A USD payment to a bank that only holds EUR requires:
- MT103 to beneficiary bank
- MT202 COV via a USD-correspondent bank
Serial vs. Cover Payments: Key Differences
| Feature | MT103 Serial | MT103 + Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Routing | Direct | Via intermediary |
| Speed | Faster (1-2 days) | Slower (2-3 days) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher (extra fees) |
| Usage | ~60% of payments | ~40% of payments |
| Security | Standard | Enhanced screening |
Data from 2023 SWIFT transaction reports
When is a Cover Payment Required?
Cover payments become necessary when:
- No Direct Relationship exists between banks
- Currency Restrictions apply (e.g., USD via CHIPS)
- Regulatory Requirements mandate intermediary checks
- High-Value Transactions (>$500k typically)
- Sanctioned Countries are involved
MT103 Cover Payment Flow Diagram
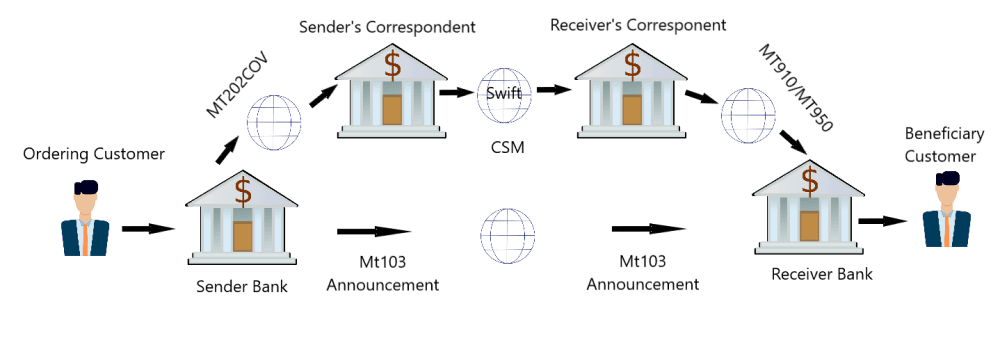
Real-World SWIFT Message Examples
MT103 Customer Credit Transfer
{1:F01SENDERBANKXXXX0000000000}
{2:O1031200010103BENEFBANKXXXX0000000000}
{3:{108:REF20240615}}
{4:
:20:TRXID20240615
:23B:CRED
:32A:240615USD100000,
:50K:/123456789
ABC CORPORATION
NEW YORK, USA
:59:/987654321
XYZ LIMITED
LONDON, UK
:71A:SHA
-}MT202 COV Cover Payment
{1:F01SENDERBANKXXXX0000000000}
{2:O2021200010103CITIUS33XXXX0000000000}
{3:{108:COVERREF20240615}}
{4:
:20:COVER20240615
:21:TRXID20240615
:32A:240615USD100000,
:52A:SENDERBANKXXXX
:58A:CITIUS33XXXX
:72:/BNF/BENEFBANKXXXX
-}Modern ISO 20022 (MX) Equivalent
The banking world is transitioning to ISO 20022, replacing MT202 COV with:
pacs.009 COV Message (XML Format)
<Document xmlns="urn:iso:std:iso:20022:tech:xsd:pacs.009.001.08">
<FIToFICstmrCdtTrf>
<GrpHdr>
<MsgId>COVER20240615</MsgId>
<CreDtTm>2024-06-15T09:30:00</CreDtTm>
</GrpHdr>
<CdtTrfTxInf>
<PmtId>
<EndToEndId>TRXID20240615</EndToEndId>
</PmtId>
<IntrBkSttlmAmt Ccy="USD">100000</IntrBkSttlmAmt>
<InstgAgt>
<FinInstnId>
<BICFI>SENDERBANKXXXX</BICFI>
</FinInstnId>
</InstgAgt>
<InstdAgt>
<FinInstnId>
<BICFI>CITIUS33XXXX</BICFI>
</FinInstnId>
</InstdAgt>
</CdtTrfTxInf>
</FIToFICstmrCdtTrf>
</Document>Key Improvements:
- Richer data fields
- Better compliance tracking
- Automated processing
Process Flow Chart of MT202/pacs.009 Cover message
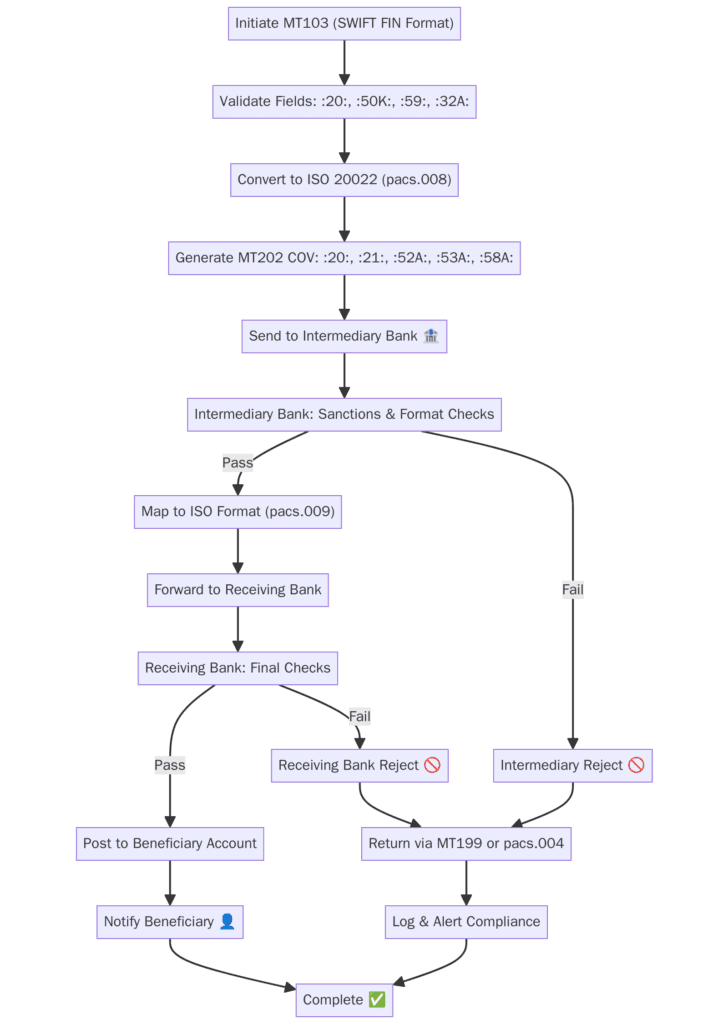
5 Key Advantages of Cover Messages
- Global Reach
Enables payments to virtually any bank worldwide, regardless of direct relationships - Enhanced Security
Multi-layer verification reduces fraud risk by 37% (SWIFT 2023 report) - Regulatory Compliance
Built-in AML and sanctions screening at intermediary banks - Currency Flexibility
Supports complex multi-currency transactions - Payment Traceability
Clear audit trail with dual-message structure
In the ISO 20022 messaging standard, pacs.009 (Financial Institution Credit Transfer) and pacs.009 COV (Cover Payment) are both used for interbank funds transfers, but they serve different purposes and have structural differences.
Key Differences Between pacs.009 and pacs.009 COV
| Tag/Field | pacs.009 (Regular FI Transfer) | pacs.009 COV (Cover Payment) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Message Purpose | Direct interbank credit transfer | Used in cover payment scenarios (e.g., MT 202-like) | COV is for intermediary bank settlements in multi-currency transactions. |
| Message Identifier | pacs.009.001.xx (e.g., 001.08) | pacs.009.001.xx but with <FwdCovInd>true</FwdCovInd> | The COV variant explicitly indicates a cover payment. |
| FwdCovInd (Forward Cover Indicator) | Not present (or false) | <FwdCovInd>true</FwdCovInd> | Mandatory in COV to distinguish it from regular pacs.009. |
| Transaction Type | Single credit transfer between FIs | Used when a separate cover payment is needed (e.g., MT 103 + MT 202) | COV ensures the intermediary bank receives funds before paying the beneficiary. |
| Intermediary Agent Usage | Rarely used | Commonly used | COV often involves an intermediary bank for currency conversion. |
| Settlement Method | Direct settlement between parties | Two-step settlement (cover first, then beneficiary payment) | COV ensures funds are pre-positioned before beneficiary payment. |
| Use Case Example | Bank A sends USD to Bank B directly | Bank A sends USD to Intermediary Bank (cover), which then sends EUR to Bank B | COV is common in FX transactions. |
Key Similarities
- Both use the pacs.009 message structure.
- Both are used for interbank transfers (not customer payments like pacs.008).
- Both support batch and single transactions.
Conclusion: Optimizing International Payments
Understanding MT103 cover payments is crucial for:
- Finance teams managing global transactions
- Banks optimizing payment routes
- Compliance officers ensuring regulatory adherence
Key Takeaways:
✔ Use serial payments for speed with known partners
✔ Choose cover payments for maximum reach and security
✔ Prepare for ISO 20022 transition with pacs.009 COV
Have questions about implementing cover payments? Share them in the comments below! We will be discussing return messages in next section.