In today’s digital-first world, payment gateways and platforms are the unsung heroes of e-commerce and online transactions. They’re the invisible bridges that connect customers, merchants, and banks, ensuring that payments are processed securely and efficiently. Whether you’re running an online store, a subscription service, or a mobile app, choosing the right payment gateway is crucial for your business’s success. In this section, we’ll explore what payment gateways are, how they work, and how to choose the best one for your needs.
Table of Contents
4.1 What is a Payment Gateway?
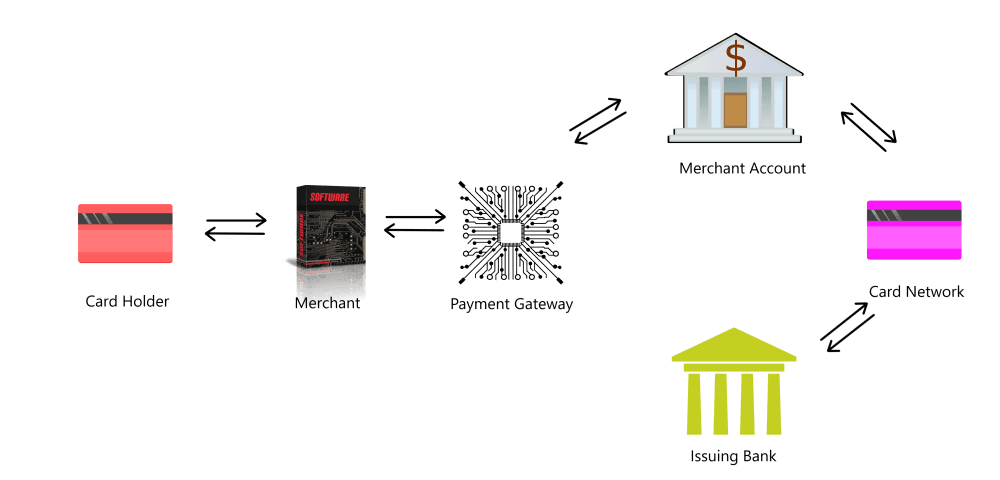
A payment gateway is a technology that facilitates online transactions by acting as the middleman between the customer, the merchant, and the financial institutions involved. Think of it as the digital equivalent of a point-of-sale (POS) terminal in a physical store. When a customer makes a purchase online, the payment gateway securely captures their payment information, sends it to the payment processor, and relays the response (approved or declined) back to the merchant.
Payment gateways are essential for e-commerce because they ensure that sensitive data, like credit card numbers, is transmitted securely. They also handle the complex process of communicating with banks and card networks to authorize and settle transactions.
4.2 How Do Payment Gateways Work?
To understand how payment gateways work, let’s walk through the steps of a typical online transaction:
- Customer Initiates Payment: The customer selects a product or service on the merchant’s website or app and proceeds to checkout. They enter their payment details (e.g., credit card number, expiration date, and CVV) into the payment form.
- Data Encryption: The payment gateway encrypts the customer’s payment information to protect it from hackers and fraudsters. This ensures that sensitive data is transmitted securely over the internet.
- Authorization Request: The encrypted data is sent to the payment processor, which forwards it to the relevant card network (e.g., Visa or Mastercard). The card network then sends the information to the customer’s bank (the issuing bank) for approval.
- Bank Approval: The issuing bank checks the customer’s account to ensure they have sufficient funds or credit. It also verifies that the transaction isn’t flagged for fraud (compliance check). If everything checks out, the bank approves the transaction and sends an authorization code back through the card network and payment processor to the payment gateway.
- Transaction Completion: The payment gateway relays the authorization code to the merchant’s website or app, confirming that the payment has been approved. The customer receives a confirmation message, and the transaction is complete.
- Settlement: At the end of the day, the payment gateway batches all approved transactions and sends them to the acquiring bank (the merchant’s bank) for settlement. The funds are then deposited into the merchant’s account, minus any fees.
This entire process typically takes just a few seconds, making it seamless for both customers and merchants. Clearing and settlement in between banks can take there own time as per the geography.
4.3 Types of Payment Gateways
Not all payment gateways are created equal. Depending on your business needs, you can choose from several types of payment gateways:
- Hosted Payment Gateways: These redirect customers to the payment gateway’s website to complete the transaction. Examples include PayPal and Stripe Checkout. Hosted gateways are easy to set up and handle security and compliance for you, but they can disrupt the customer experience by taking them away from your website.
- Self-Hosted Payment Gateways: These allow customers to enter their payment details directly on your website. The data is then sent to the payment gateway for processing. Self-hosted gateways give you more control over the checkout experience but require you to handle security and compliance, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
- API-Hosted Payment Gateways: These use APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to integrate the payment gateway directly into your website or app. Examples include Stripe and Adyen. API-hosted gateways offer a seamless checkout experience and give you full control over the design and functionality of your payment page.
- Local Bank Integration: In some regions, businesses integrate directly with local banks to process payments. This is common in countries with unique payment systems, such as India’s UPI or Brazil’s PIX.
4.4 Key Features to Look for in a Payment Gateway

Choosing the right payment gateway is a critical decision for your business. Here are some key features to consider:
- Security: Look for a payment gateway that offers robust security features, such as encryption, tokenization, and fraud detection. It should also be PCI DSS compliant to ensure the safe handling of sensitive data.
- Supported Payment Methods: Make sure the gateway supports the payment methods your customers prefer, such as credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay), and local payment options.
- Global Reach: If you sell internationally, choose a payment gateway that supports multiple currencies and cross-border transactions. This will help you reach a global audience and reduce conversion friction.
- Ease of Integration: The gateway should be easy to integrate with your website, app, or e-commerce platform. Look for plugins, APIs, and developer-friendly documentation.
- Transaction Fees: Compare the fees charged by different payment gateways, including setup fees, transaction fees, and monthly fees. Keep in mind that lower fees don’t always mean better value—consider the overall features and reliability.
- Customer Support: Choose a payment gateway with reliable customer support, including 24/7 availability, live chat, and phone support. This is especially important if you’re new to online payments or run a high-volume business.
- Scalability: Your payment gateway should be able to grow with your business. Look for a solution that can handle increasing transaction volumes and support new features as your needs evolve.
4.5 Top Payment Gateways in 2025
Here’s a quick overview of some of the most popular payment gateways available today as per my research, if there are any better do comment:
- Stripe: Known for its developer-friendly APIs and global reach, Stripe is a favorite among startups and large enterprises alike. It supports a wide range of payment methods and currencies.
- PayPal: One of the most widely recognized payment gateways, PayPal is easy to use and offers a seamless checkout experience. It’s ideal for small businesses and freelancers.
- Square: Square is a great option for businesses that operate both online and offline. It offers a range of tools, including POS systems and invoicing software.
- Adyen: Adyen is a global payment platform that supports over 250 payment methods and 150 currencies. It’s popular among large enterprises and multinational companies.
- Authorize.Net: A veteran in the payment industry, Authorize.Net is known for its reliability and robust security features. It’s a good choice for businesses of all sizes.
- Razorpay: Popular in India, Razorpay supports UPI, net banking, and other local payment methods. It’s ideal for businesses targeting the Indian market.
4.6 Challenges of Using Payment Gateways
While payment gateways offer many benefits, they also come with challenges:
- Fees: Payment gateways charge fees for their services, which can eat into your profit margins. Be sure to factor these costs into your pricing strategy.
- Technical Issues: Payment gateways rely on technology, which means they’re susceptible to downtime and technical glitches. Choose a reliable provider with a strong track record.
- Fraud: Online payments are a prime target for fraudsters. Make sure your payment gateway offers robust fraud prevention tools.
- Regulatory Compliance: Payment gateways must comply with various regulations, such as PCI DSS and GDPR. Ensure your chosen gateway meets these requirements.
4.7 The Future of Payment Gateways
The payment gateway industry is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. Here are some trends to watch:
- Omnichannel Payments: Payment gateways are increasingly supporting omnichannel payments, allowing businesses to accept payments online, in-store, and via mobile apps seamlessly.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are being used to improve fraud detection, personalize the checkout experience, and optimize payment processes.
- Blockchain Integration: Some payment gateways are exploring blockchain technology to enable faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions.
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL): BNPL options are becoming increasingly popular, and many payment gateways are integrating this feature to attract more customers.
Conclusion
Payment gateways are the backbone of online commerce, enabling businesses to accept payments securely and efficiently. Whether you’re a small business owner or a large enterprise, choosing the right payment gateway is essential for providing a seamless checkout experience and building trust with your customers.
In the next section, we’ll dive into Payment Security and Compliance, exploring how to protect your business and customers from fraud and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Stay tuned!